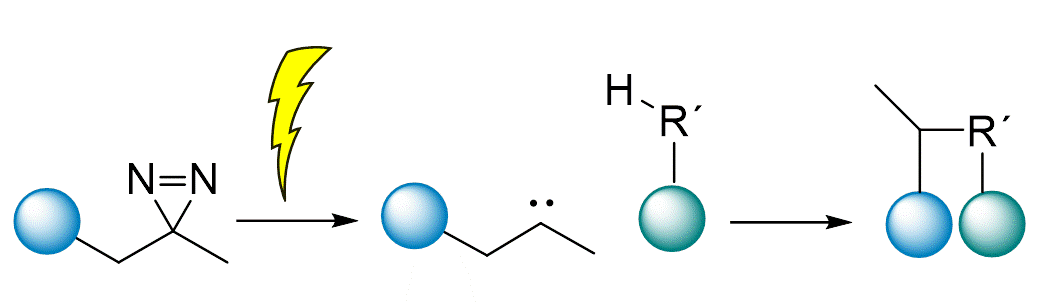
In order to study identity, function, location, transport and interacting proteins of lipids, trifunctional lipid (TFL) derivatives provide the ideal tool to answer your research questions. The combination of three functional groups allows for excellent temporal control of lipid release through uncaging, protect from wash-out in fixed samples and covalent connections to binding proteins through orthogonal photo-crosslinking, and isolation or fluorescent tagging of protein-lipid conjugates through click chemistry.
TFLs are ideally suited to study
- intracellular lipid localization
- lipid−protein interactions
- lipid metabolism
with a single tool, that combines a photo-removable protecting group (cage), a photo-crosslinkable diazirine group and a terminal alkyne group useful for click chemistry in live cells.
Flash & Click Tools you will find here
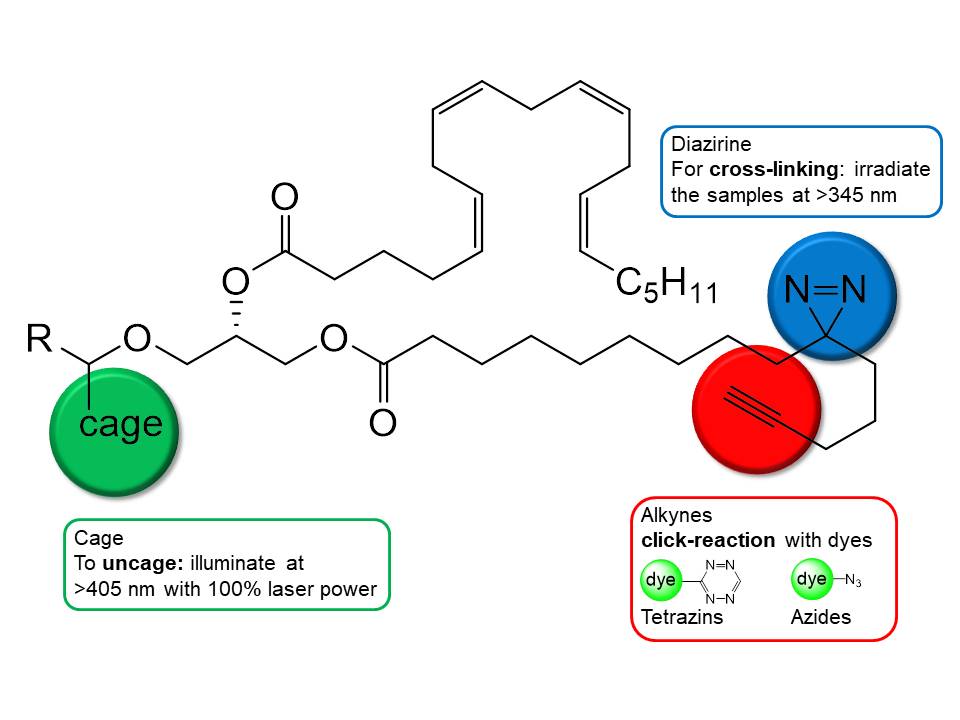
trifunctional lipids